生态产品市场金融化还需要相应的法律法规监管的支持 , 以欧盟碳市场为例 ,欧盟通过《 金融工具市场指令》( Markets in Financial Instruments Directive, MiFiD) 、修订的《 金融工具市场指令》(Markets in Financial Instruments DirectiveI II, MiFiD II)、《市场滥用指令》( Market Abuse Directive, MAD) 、《透明度指令》(Transparency Directive, TD)等金融市场监管法规逐步将碳配额现货和衍生品市场纳人金融监管体系 ,明确了碳配额的金融属性。
从推进生态产品价值外部性内部化的零星市场创新 ,到经济和金融体系能够兼顾生态目标 ,除了需要基于生态产品的金融产品与服务创新之外 ,还需要各类金融机构充分认知和量化生态风险。2020 年普华永道与世界自然基金会共同发布了《大自然不容有失—金融机构需要管理生物多样性风险》③ ,呼吁市场服务机构开发评估工具 ,用于评估其业务体系与生态系统的双向依赖和影响 , 将生态风险纳人其行为决策 。在宏观金融监管层面 ,央行和金融监管机构若能将生态风险纳人宏观审慎工具、货币政策工具及绿色金融指引 ,将对生态产品价值在经济系统中的主流化起到根本性的支撑作用 。而政策性金融机构则可以发挥其在资金、能力建设、知识与技术推广、中长期优惠贷 款等方面的优势和作用 ,开发、应用和推广支持生态产品价值实现的绿色金融工具 ,从而撬动规模化的私人投资 ,并对规模化的生态投融资模式发展起到示范作用④。
基于绿色金融的生态产品价值实现实践进展与机制分析
( 一 )基于绿色金融的生态产品价值实现实践进展
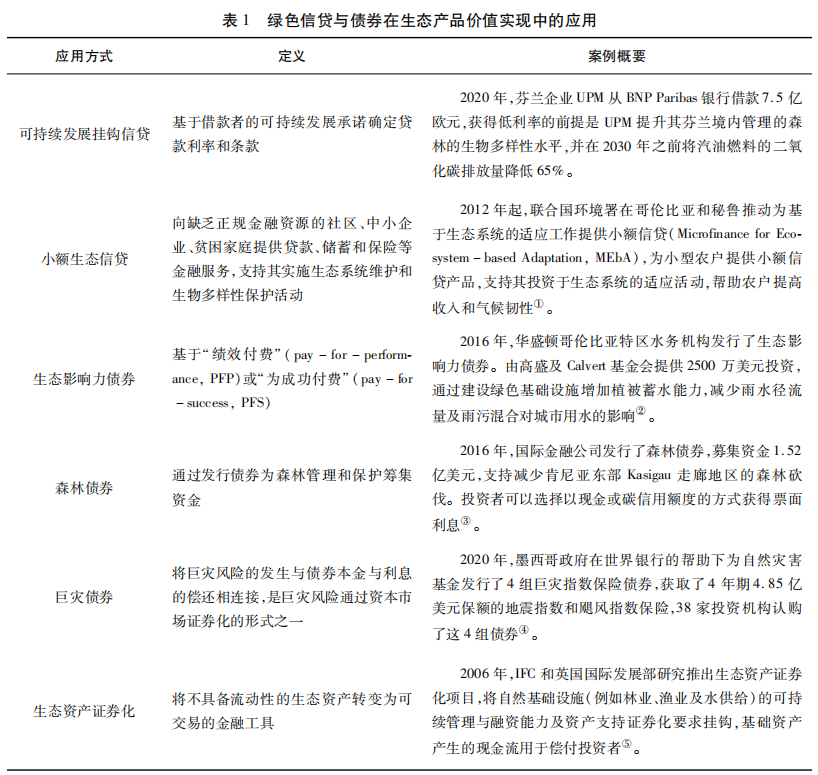
本研究梳理了近年来基于绿色金融的生态产品价值实现的典型案例 。其中 ,生态产品投融资模式主要有可持续发展挂钩信贷(Sustainability-linked Loan) 、小额生态信贷( Microfinance for Eco-system) 、生态影响力债券( Environmental/Social Impact Bond) 、森林债券( Forest Bond) 、巨灾债券(Catastrophe Bond) 、生态资产证券化(Ecological Aset-backed Securities) ,如表 1 所示。
引用注释:①ThomasHahn , ConstanceMcDermot, ClaudiaItuarte-Lima, Mariaschultz, TomGreen , Purposesand Degresof Commodification: EconomicInstrumentsforBiodiversityand EcosystemservicesNeed NotReplyon MarketsorMonetary Valuation , Ecosystemser⑦ices,Vol.16 ,No.12 ,2015 ,pp.74 -82 .
②张黎黎:《透视我国碳市场发展》,《中国金融》, 2021 年第 5 期。
③PwC, wwF, NatureIstoBigtoFail- Biodiversity: theNextFrontierinFinancialRisk Management,https:/ wfint.awsasets.panda.org/downloads/natureistobigtofailen web.pdf,2020 -01 -21 .
④AndrewDeutza, GeofreyM.Healb, etal., FinancingNature: ClosingtheGlobalBiodiversityFinancingGap , ht- tps:/w.paulsoninstitute.org/wp -content/uploads/2020/09/FNANCING-NATURE Ful-ReportFinal-Version 091520 .pdf, 2020 -09 -15 .
引用注释:①German societyforInternationalCooperation (GIZ) ,Finance0ptionsand InstrumentsforEcosystem-Based Adap- tation , 0verviewand Compilation ofTen Examples, https:/w.adaptationcommunity.net/wp -content/uploads/2018/ 06/giz2018 -en -eba-finance-guidebook -low-res.pdf, 2018 -06 -28 .
②Quantified Ventures.Casestudy: DCwater.https:/static1.squarespace.com/static/5d5b210885b4ce0001663c2 5/t/5e136b61f2afef61e95e7472/1578331001269/DC+water+Case+studyQuantified+Ventures, 2018 -10 -12 .
③AndrewDeutza, GeofreyM.etal., ClosingtheGlobalBiodiversityFinancingGap , https:/w.paulsoninstitute. org/wp -content/uploads/2020/09/FNANCING-NATUREFul-ReportFinal-Version 091520 .pdf, 2020 -09 -15 .
④world Bank , Casestudy: InsuringMexicoAgainstNaturalDisasters, https://pubdocs.worldbank.org/en/ 737151585254940284/F0NDEN-Mexico-Cat-Bond -Case-study-3 -4 -2020 -final.pdf, 2020 -04 -03 .
⑤United NationsEnvironmentProgrammeFinanceInitiative(UNEPFI) , Green FinancialProductsand services: Cur- rentTrendsand Future0pportunitiesinNorthAmerica, https:/w.unepfi.org/fileadmin/documents/greenprods01 . pdf, 2007 -08 -15 .
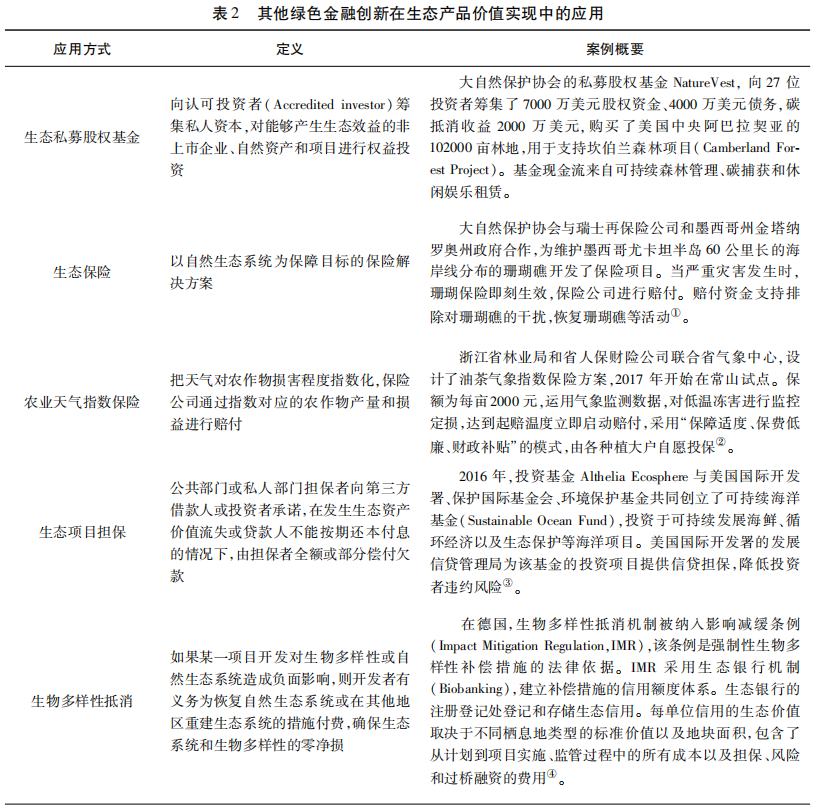
其他应用于生态产品价值实现的绿色金融创新包括多种形式的生态基金 ,如生态私募股权基金(Private Equity Fund);降低生态风险和增信的创新实践 ,如生态保险(Ecosystem Insurance)、农业天气指数保险(Index-based Weather Insurance for Agriculture)、生态项目担保(Ecological Project Guarantee);打造新的交易模式与市场 ,如生物多样性抵消(Biodiversity 0ffset)、债务自然互换( Debt-for-Nature Swap)和碳排放交易机制(Emision Trading Scheme)(见表2) 。以上探索初步为我国绿色金融系统支持生态产品价值实现提供了可资借鉴的模式和路径。
引用注释:①TheNatureConservancy, EnvironmentalFinance, Investinginnature: privatefinancefornature-based resilience, https://downloads. ctfasets. net/4cgqlwde6qy0/5mA60ARJcp8Euh7BJb6Gzm/11124891d26f4f3c3f11a53d2cb28b6c/ TNC Investingin Nature 2019 .pdf, 2019 -11 -26 .
②浙江省林业局:《 油茶气象指数保险为林农收益系上保险索》, http:/lyj.zj.gov.cn/art/2021/4/20/art 1277871 59008915 .html,2021 年 4 月 20 日。
③AndrewDeutza, GeofreyM.Healbetal., FinancingNature: ClosingtheGlobalBiodiversityFinancingGap , ht- tps:/w.paulsoninstitute.org/wp -content/uploads/2020/09/FNANCING-NATURE Ful-ReportFinal-Version 091520 .pdf, 2020 -09 -15 .
编辑:李丹
版权声明:
凡注明来源为“中国水网/中国固废网/中国大气网“的所有内容,包括但不限于文字、图表、音频视频等,版权均属E20环境平台所有,如有转载,请注明来源和作者。E20环境平台保留责任追究的权利。
媒体合作请联系:李女士 010-88480317
